ASTM F136 Grade 23 Ti-6Al-4V Eli Alloyed Titanium Wire for Dental Implants
Ti-Gr. 5: Recommended for high mechanical resistance applications up to 350° -400°C, it combines an ideal set of properties: high tensile strength, low density, toughness and ductility, weldability and machinability comparable to austeni1ic stainless steel.
Suitable to solution and precipitation heat treatments.
Ti-Gr. 5 Eli: Ti6Al4V with extra low interstitial elements content, with enhanced ductility, typically used in the non aged condition for maximum toughness. Widely used for cryogenic devices as well as medical applications.
Product specification:
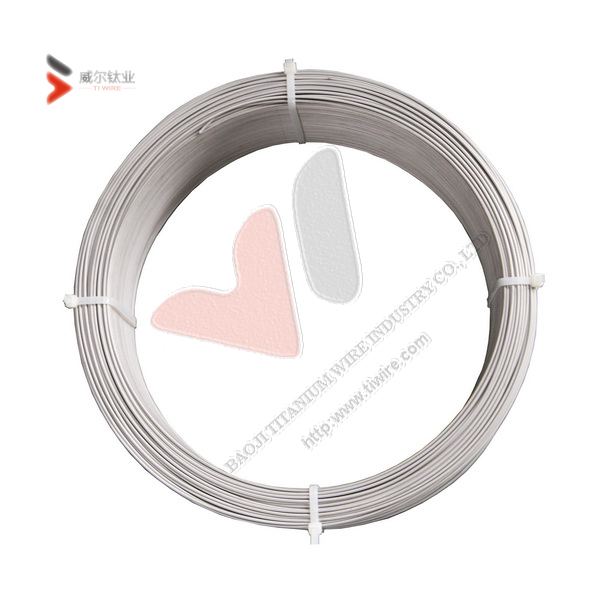
Diameter: 0.15 mm-6.0 mm
Weight: Approx 35 kilogrames
Shape: In coil or spool
Surface treatment: Polished, pickled, peeled
Grade status: Grade 5 Ti-6Al-4V, Grade 23 Ti-6Al-4V Eli
Standard: ASTM F136, ASTM B863, ASTM 2965, ASTM 3623, AMS 4928
Product status: Heat processing (R), cold processing (Y), annealed (M)
Features:
Low density and high strength
Exceptional corrosion resistance
Excellent elevated temperature properties
Excellent Bearing to cryogenic property
Essentially non-magnetic
Nontoxic, non-allergenic and fully biocompatible
Good thermal properties
Low modulus of elasticity
Low thermal expansion coefficient
High melting point
Excellent aesthetic qualities
Environmentally sound
Production capability: 72 Metric Tons
Packing:
In Coil: Protected by foam paper+ plywood case.
In spool: Carton box + plywood case.
Delivery time: 5-25 days
Shipping: By international express (TNT, FEDEX, DHL, UPS, etc.), By Air, By Sea
Trade terms: FOB China, CIF, DDP
Payment terms: T/T, L/C, PayPal, Western Union
![]() Titanium for surgical implants.pdf
Titanium for surgical implants.pdf

ASTM F136 Grade 23 Ti-6Al-4V Eli Alloyed Titanium Wire for Dental Implants
Titanium is a strong, lightweight, silver-gray metal that is found fairly commonly in igneous rocks and geological deposits. Titanium has a number of impressive properties, including the ability to bind with human bone in a process called biointegration or osseointegration. Because of this, and the fact that the body will not reject it, this metal can be used for a number of medical and dental purposes. Hip and knee replacements, for example, often involve the use of a titanium implant.
The field of dentistry is increasingly finding use for titanium implants as well. A titanium implant for dental use will typically consist of a screw which resembles the root of a tooth and has either a smooth or roughened surface. The “root” is placed in the jawbone and the process of osseointegration is allowed to take place for several weeks or months. At the appropriate time, a dentist will then attach a crown to the root. Because the root is already integrated, the patient is then immediately able to use the new implant as if it were a natural tooth.
Chemical Compositions:
| Element | Composition, % |
| Nitrogen, max | 0.05 |
| Carbon, max | 0.08 |
| Hydrogen, max | 0.012 |
| Iron, max | 0.25 |
| Oxygen, max | 0.13 |
| Aluminum | 5.5–6.50 |
| Vanadium | 3.5–4.5 |
| Titanium | balance |
Mechanical Properties:
| Nominal diameter or distance between parallel sides, in (mm) | Tensile strength min,psi (MPa) | Yield Strength (0.2 % offset) min, psi (MPa) | Elongation in 4D or 4W min, % | Reduction of area min, % | ||||
| L | LT | ST | L | LT | ST | |||
Under 0.187 (4.75) thickness or diameter | 125,000 (860) | 115,000 (795) | 10 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
0.187 (4.75) to under 1.75 (44.45), incl | 125,000 (860) | 115,000 (795) | 10 | -- | -- | 25 | -- | -- |
1.75 (44.45) to under 2.50 (63.50), incl | 120,000 (825) | 110,000 (760) | 8 | -- | -- | 20 | -- | -- |
2.50 (63.50) to 4.00 (101.60), incl | 120,000 (825) | 110,000 (760) | 8 | 8 | 8 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Bend Testing | ||||||||
Under 0.070 (1.778) in thickness | 9 T | |||||||
0.070 (1.778) to 0.187 (4.75), incl | 10 T | |||||||