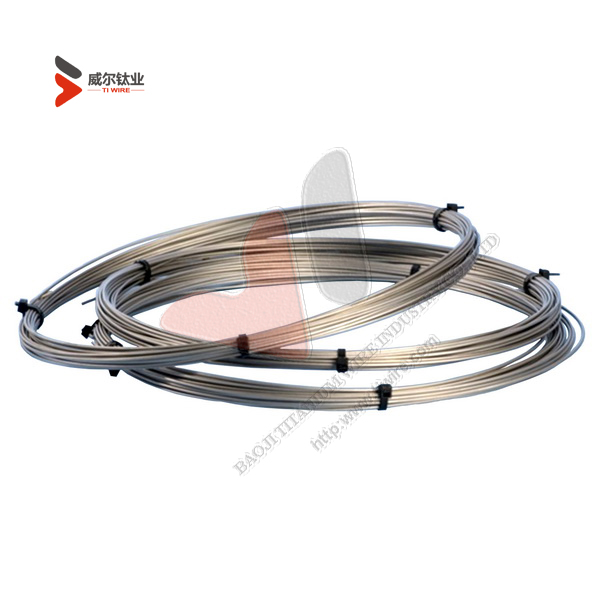
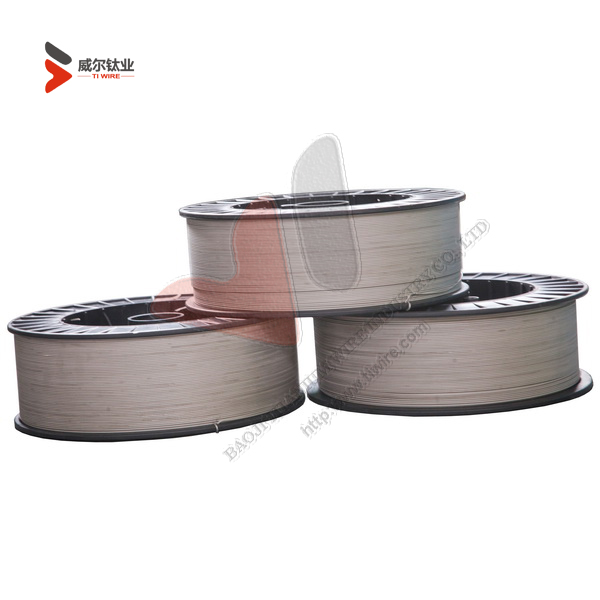
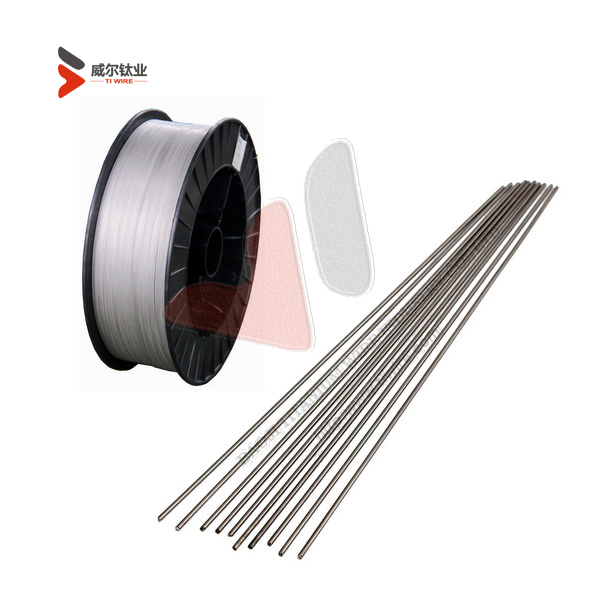
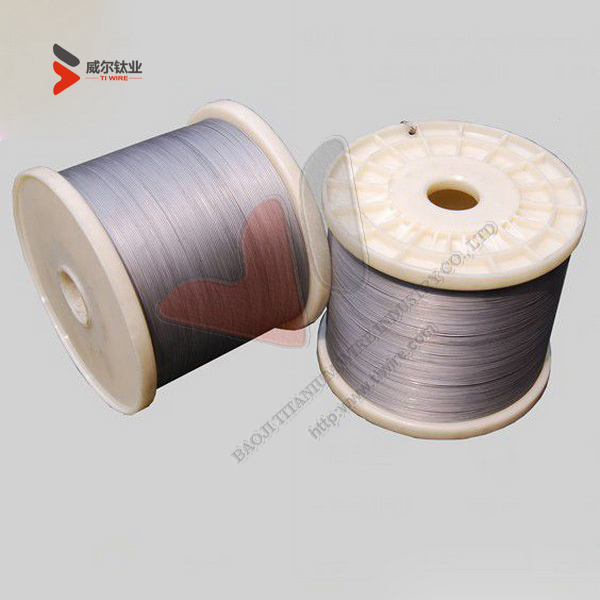
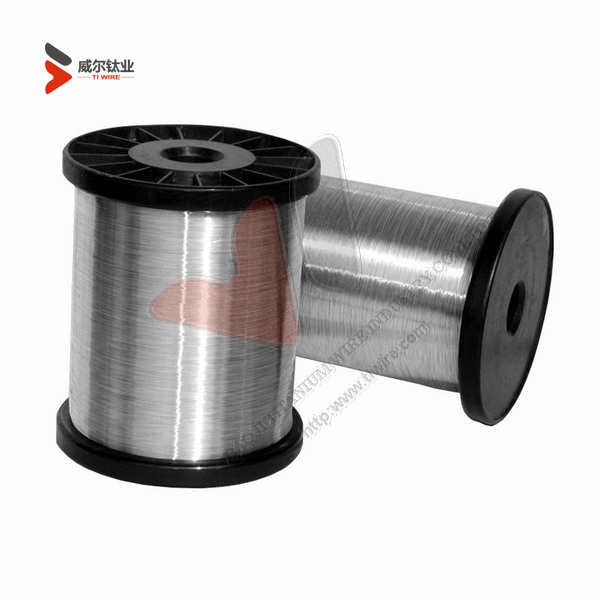
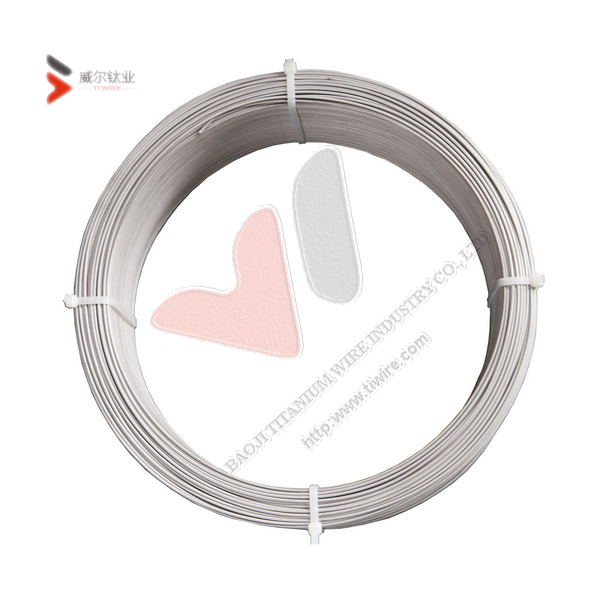
ASTM F67 Grade 1 and 2 Pure Titanium Wire for Dental Implants
Ti-Gr. 1: the very low content of oxygen creates a reduced tensile strength and high ductility as well as excellent corrosion resistance in bland reducing to strongly oxidazing environments.
Availability upon minimum production lot quantity
Ti-Gr. 2: This grade is considered the most commonly used in industrial service, offering a good combination of high corrosion and erosion resistance, good cold formability and excellent weldability. Compared to Ti-Gr.1 it shows a higher oxygen content and tensile strength.
Product specification:
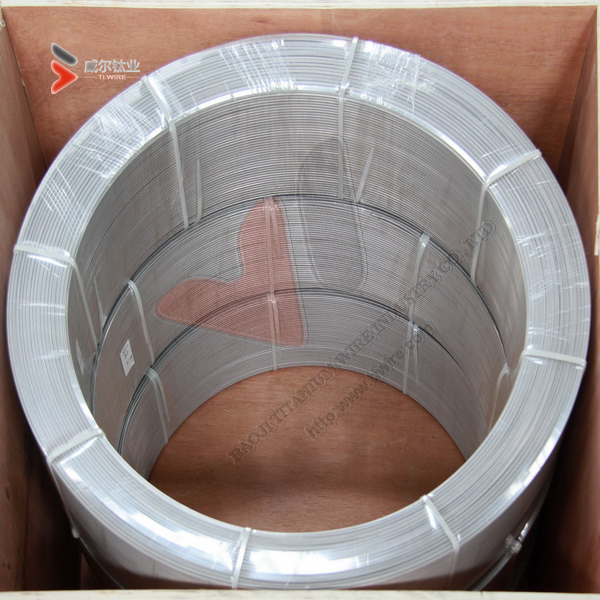
Diameter: 3.175 mm, 6.35 mm
Weight: approx 50 kilogrames
Shape: In coil
Surface treatment: pickled, peeled
Grade status: Grade 1, Grade 2
Standard: ASTM F67, ASTM B863, ASTM 2965, ASTM 3623, AMS 4928
Product status: heat processing (R), cold processing (Y), annealed (M)
Features:
Low density and high strength
Exceptional corrosion resistance
Excellent elevated temperature properties
Excellent Bearing to cryogenic property
Essentially non-magnetic
Nontoxic, non-allergenic and fully biocompatible
Good thermal properties
Low modulus of elasticity
Low thermal expansion coefficient
High melting point
Excellent aesthetic qualities
Environmentally sound
Application:
Electrode materials, fasteners, welding materials, medical field, surgical implants, chemical industry, structural parts,
glasses, aerospace and marine, consumer and architectural, jewelry, nuclear waste storage, etc.
Production capability: 72 Metric Tons
Packing:
In Coil: Protected by foam paper+ plywood case.
Delivery time: 5-25 days
Shipping: By international express (TNT, FEDEX, DHL, UPS, etc.), By Air, By Sea
Trade terms: FOB China, CIF, DDP
Payment terms: T/T, L/C, PayPal, Western Union

ASTM F67 Grade 1 and 2 Pure Titanium Wire for Dental Implants
Titanium is a strong, lightweight, silver-gray metal that is found fairly commonly in igneous rocks and geological deposits. Titanium has a number of impressive properties, including the ability to bind with human bone in a process called biointegration or osseointegration. Because of this, and the fact that the body will not reject it, this metal can be used for a number of medical and dental purposes. Hip and knee replacements, for example, often involve the use of a titanium implant.
The field of dentistry is increasingly finding use for titanium implants as well. A titanium implant for dental use will typically consist of a screw which resembles the root of a tooth and has either a smooth or roughened surface. The “root” is placed in the jawbone and the process of osseointegration is allowed to take place for several weeks or months. At the appropriate time, a dentist will then attach a crown to the root. Because the root is already integrated, the patient is then immediately able to use the new implant as if it were a natural tooth.
Chemical Compositions:
| Element | CompositionA, % (mass/mass) | |||
| Grade 1 UNS R50250 | Grade 2 UNS R50400 | Grade 3 UNS R50550 | Grade 4 UNS R50700 | |
| Nitrogen, max | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Carbon, max | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Hydrogen, max | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
| Iron, max | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.50 |
| Oxygen, max | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
| Titanium | balance | balance | balance | balance |
Mechanical Property:
| Grade | Tensile Strength(min) | Yeild Strength(min) | Elongation in 4D, min, % | Reduction of Area, min, % | ||
| ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | |||
| Grade 1 | 35 | 240 | 20 | 138 | 24 | 30 |
| Grade2 | 50 | 345 | 40 | 275 | 20 | 30 |
| Grade 3 | 65 | 450 | 55 | 380 | 18 | 30 |
| Grade 4 | 80 | 550 | 70 | 483 | 15 | 25 |